Send Webhooks Quickstart
In this quickstart, you'll learn how to send webhooks to customer endpoints using Hookdeck. You'll achieve this by creating a Connection consisting of a Source to be used to trigger the event to be sent to user endpoints represented by one or more Destination.

You will walk through these steps:
- Ensure you have some prerequisites in place before you begin
- Create a webhook subscription, represented by a Connection within Hookdeck
- Send a test webhook via Hookdeck
- Send a webhook to your local development server via Hookdeck
- Send a webhook to a public URL via Hookdeck
Before you begin
Signup for a Hookdeck account and create a Hookdeck Organization.
Get the API key from your project secrets.
Install the Hookdeck CLI and run hookdeck login.
Create a webhook subscription
A Connection consists of a Source, optional Rules, and a Destination. It defines the flow of the webhook event, from receipt through to delivery. When sending webhooks, a Connection represents a webhook subscription.
From the Connections section of the Hookdeck dashboard, click the button in the top-right of the page.
In the Create Connection page, under Configure a Source, enter account-123 as the Name. Under Source Type select Hookdeck Publish API. A source of this type can only be used to publish webhook events using the Publish API.
Under Configure a Destination enter the Name endpoint-123 and set the Destination Type to HTTP, and set the URL to https://mock.hookdeck.com.
Within the Set Connection Name enter account-123-endpoint-123.
Click the button to create the Connection and close the Connection Created dialog that appears by clicking the button.
Run the following command to create a Connection within your Hookdeck project:
hookdeck connection create \
--name "account-123-endpoint-123" \
--source-type PUBLISH_API --source-name "account-123" \
--destination-type MOCK_API --destination-name "endpoint-123"
The CLI command creates a Connection named account-123-endpoint-123. The Source has the name account-123 and is of type PUBLISH_API which means webhook events can only be published using the Publish API. The Destination has the name endpoint-123 and uses Hookdeck's Mock API (https://mock.hookdeck.com). The mock endpoint is a destination you can use for testing that receives the HTTP request and returns a 200 response by default.
You will see output similar to the following:
Connection created successfully
Connection ID: web_oPymMJ0isyuS
Source ID: src_KUdNgMByl0uP
Source URL: https://hkdk.events/v1/publish
Destination ID: des_wNYxQXpkYHcM
The CLI command has created a connection.
Run the following command to create a Connection within your Hookdeck project:
curl --location 'https://api.hookdeck.com/2025-07-01/connections' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PROJECT_API_KEY" \
--data '{
"name": "account-123-endpoint-123",
"source": {
"name": "account-123",
"type": "PUBLISH_API"
},
"destination": {
"name": "endpoint-123",
"type": "MOCK",
"config": {
"url": "https://mock.hookdeck.com"
}
}
}'
The cURL command creates a Connection named account-123-endpoint-123. The Source has the name account-123 and is of type PUBLISH_API which means webhook events can only be published using the Publish API. The Destination has the name endpoint-123 is of type HTTP and has a config.url value of https://mock.hookdeck.com. The mock endpoint is a destination you can use for testing that receives the HTTP request and returns a 200 response by default.
The response will be formatted as follows:
{
"id": "web_oPymMJ0isyuS",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.897Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:44.096Z",
"paused_at": null,
"name": "account-123-endpoint-123",
"rules": [],
"description": null,
"destination": {
"id": "des_wNYxQXpkYHcM",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"type": "HTTP",
"config": {
"url": "https://mock.hookdeck.com",
"rate_limit": null,
"rate_limit_period": "second",
"path_forwarding_disabled": false,
"http_method": null,
"auth_type": "HOOKDECK_SIGNATURE",
"auth": {}
},
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.897Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.903Z",
"name": "endpoint-123",
"description": null
},
"source": {
"id": "src_KUdNgMByl0uP",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.897Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.905Z",
"name": "account-123",
"type": "PUBLISH_API",
"config": {
"allowed_http_methods": ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"],
"custom_response": null,
"auth_type": null,
"auth": null
},
"description": null,
"url": "https://hkdk.events/v1/publish",
"authenticated": false
},
"full_name": "account-123 -> account-123-endpoint-123"
}
The cURL command has created a connection.
account-123 represents a unique account ID within your system. endpoint-123 represents a unique endpoint for the developer registering a webhook with you. account-123-endpoint-123 is a unique name for the Connection combining the account and endpoint names.
Open the Connections section for your project in the Hookdeck dashboard to see the visual representation of the connection you created.
Publish a test outbound webhook via Hookdeck
Make a POST request to the Publish API endpoint, passing the Source name in a X-Hookdeck-Source-Name HTTP header:
curl --location 'https://hkdk.events/v1/publish' \
--header 'X-Hookdeck-Source-Name: account-123' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PROJECT_API_KEY" \
--data-raw '{
"type": "order.created",
"timestamp": "2023-11-18 17:23:30",
"email": "customer@example.com",
"description": "Growth plan",
"plan_id": "growth",
"payment_status": "pending"
}'
The response will look similar to the following:
{
"status": "SUCCESS",
"message": "Request successfully handled. Request ID: req_pSO2eEXILyN4CxxphL3I",
"request_id": "req_pSO2eEXILyN4CxxphL3I"
}
The status with a value of SUCCESS indicates that Hookdeck has successfully ingested the HTTP request.
Open the Requests section of Hookdeck dashboard to see the request within the UI.
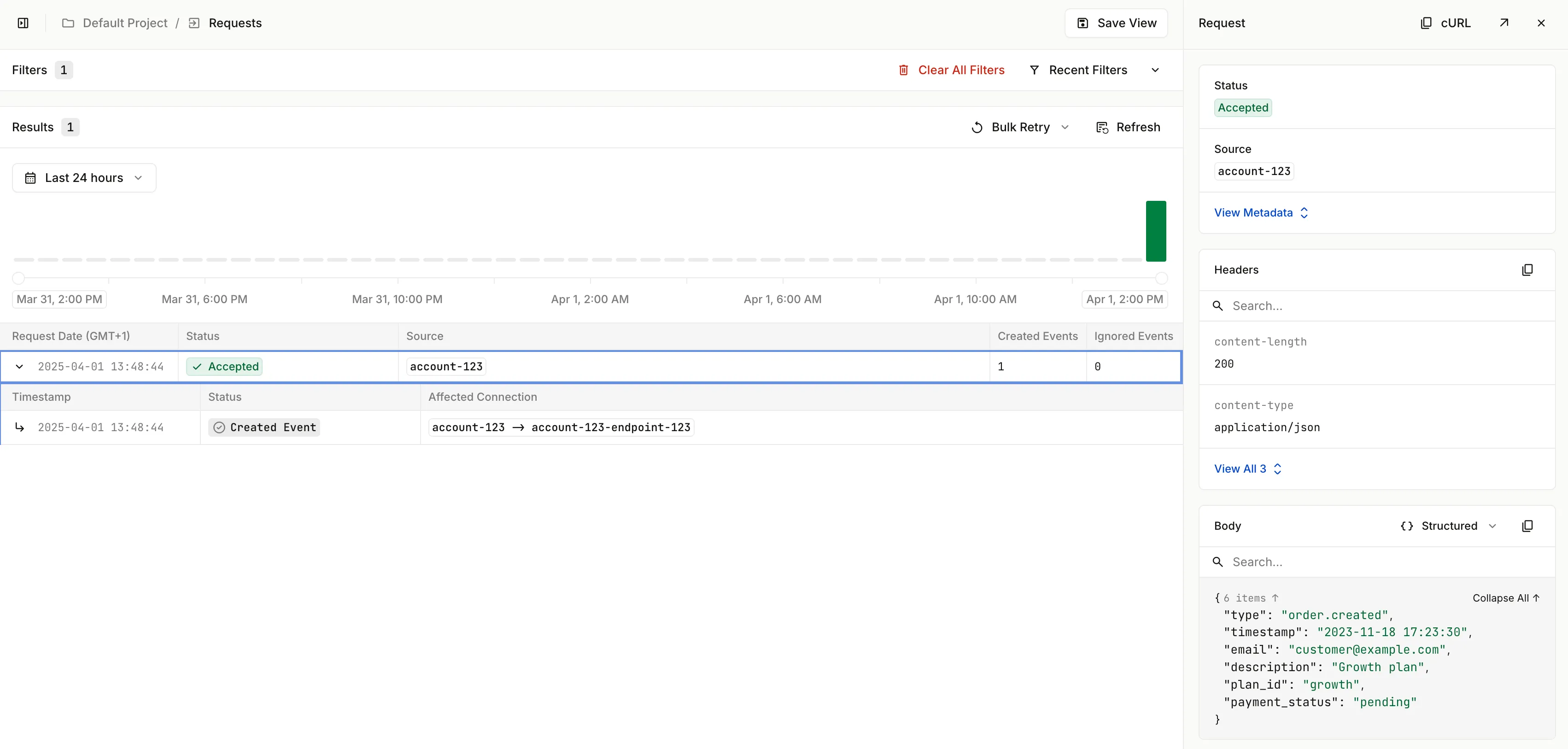
Next, open the Events section of the Hookeck dashboard. Click on the Event to expand the section to see the Attempts made to deliver the event to a webhook endpoint.
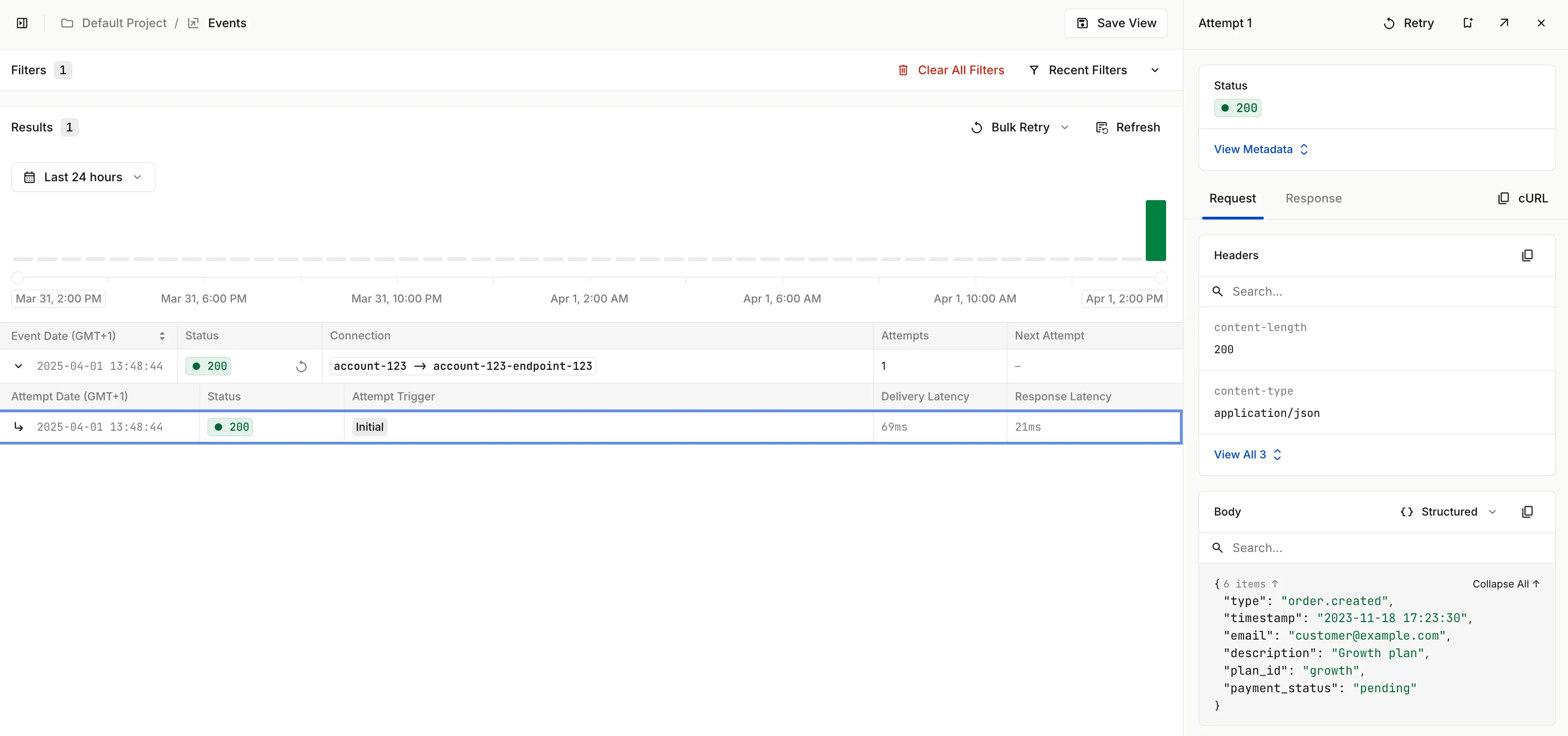
Publish a webhook to your local development server via Hookdeck
To receive a webhook locally, first start your local development server:
Run the following to get the code and install the app's dependencies:
npx degit hookdeck/quickstarts/typescript/inbound hookdeck-inbound
cd hookdeck-inbound
npm i
Then, run the application:
npm run dev
You will see output as follows:
> inbound@1.0.0 dev
> nodemon index.ts
[nodemon] 3.0.1
[nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs`
[nodemon] watching path(s): *.*
[nodemon] watching extensions: ts,json
[nodemon] starting `ts-node index.ts`
🪝 Server running at http://localhost:3030
Get the Hookdeck quickstart code:
git clone https://github.com/hookdeck/quickstarts.git
cd quickstarts/python/inbound
Create a new virtualenv, activate it, and Install the application dependencies:
virtualenv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the app:
python app.py
The output will look as follows:
python app.py
* Serving Flask app 'app'
* Debug mode: on
INFO:werkzeug:WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000
INFO:werkzeug:Press CTRL+C to quit
INFO:werkzeug: * Restarting with stat
WARNING:werkzeug: * Debugger is active!
INFO:werkzeug: * Debugger PIN: 530-477-256
Get the Hookdeck quickstart code:
git clone https://github.com/hookdeck/quickstarts.git
cd quickstarts/go/inbound
Run the app:
go run .
The output will look as follows:
go run .
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] POST /webhook --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers)
🪝 Server running at http://localhost:3030[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :3030
Next, use the Hookdeck CLI to create a connection to route events from the account-123 Source to the local development server. For the next step, you'll need to know the port your dev server is listening on.
Assuming your dev server is running on port 3030, run the following command:
hookdeck listen 3030 account-123 --path /webhook
You will see a command output similar to the following:
Dashboard
👉 Inspect and replay events: https://dashboard.hookdeck.com?team_id=tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI
account-123 Source
🔌 Event URL: https://hkdk.events/v1/publish
Connections
local forwarding to /webhook
> Ready! (^C to quit)
Open the Connections section for your project in the Hookdeck dashboard to see the Hookdeck CLI within the visual representation of the connection.
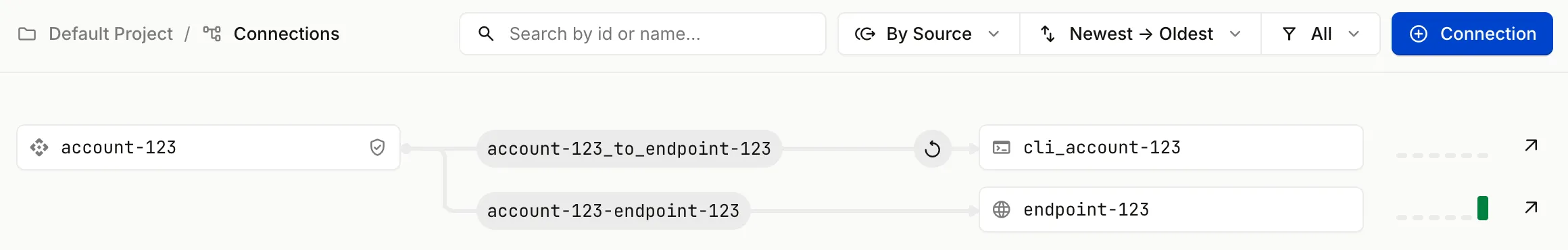
With your dev server running and the Hookdeck CLI set up to listen to events from the account-123 source, you can test receiving a webhook on your app running on your localhost via Hookdeck using the Hookdeck Publish API:
curl --location 'https://hkdk.events/v1/publish' \
--header 'X-Hookdeck-Source-Name: account-123' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PROJECT_API_KEY" \
--data-raw '{
"type": "order.updated",
"timestamp": "2023-11-18 17:23:30",
"email": "customer@example.com",
"description": "Growth plan",
"plan_id": "growth",
"payment_status": "paid"
}'
After running the cURL command, you will see the request logged by the Hookdeck CLI:
2023-11-19 20:36:53 [200] POST http://localhost:3030/webhook | https://dashboard.hookdeck.com/cli/events/evt_YhWPqX1QNKZrrrcybI
You'll also see the request logged by your development server:
{
webhook_received: '2023-11-19T20:40:29.767Z',
body: {
type: 'order.updated',
timestamp: '2023-11-18 17:25:15',
email: 'customer@example.com',
description: 'Hookdeck Growth plan',
plan_id: 'growth',
payment_status: 'paid'
}
}
INFO:app:webhook_received 2023-11-19T20:40:29.767Z {
"type": "order.updated",
"timestamp": "2023-11-18 17:25:15",
"email": "customer@example.com",
"description": "Hookdeck Growth plan",
"plan_id": "growth",
"payment_status": "paid"
}
INFO:werkzeug:127.0.0.1 - - [19/Nov/2023 20:36:53] "POST /webhook HTTP/1.1" 200 -
2024/01/12 16:41:45 webhook_received: {
type: 'order.updated',
timestamp: '2023-11-18 17:25:15',
email: 'customer@example.com',
description: 'Hookdeck Growth plan',
plan_id: 'growth',
payment_status: 'paid'
}
Open the Events section with the CLI view selected, click on the event, and you can inspect various details about the event including the HTTP response from your local server in the expanded panel on the right-hand side.
Publish a webhook to a the developer's webhook URL via Hookdeck
This step assumes you have an application deployed that you want to receive a webhook.
Next, update the Destination URL for your account-123-endpoint-123 to a public webhook URL.
From the Connection section, click on the endpoint-123 Destination and click the button.
In the Destination page, scroll down to the Configuration section. Change the Destination Type to HTTP and update the URL to the developer's webhook receving URL and click .
Run the following command to update your connection:
hookdeck connection upsert account-123-endpoint-123 \
--destination-url <YOUR_WEBHOOK_URL>
The CLI command updates the Connection named account-123-endpoint-123 and changes the destination URL to your specified webhook URL.
You will see output similar to the following:
Connection updated successfully
Connection ID: web_oPymMJ0isyuS
Destination URL updated to: {YOUR_WEBHOOK_URL}
Run a PUT request to update your connection:
curl --location --request PUT 'https://api.hookdeck.com/2025-07-01/connections' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PROJECT_API_KEY" \
--data '{
"name": "account-123-endpoint-123",
"source": {
"name": "account-123"
},
"destination": {
"name": "endpoint-123",
"type": "HTTP",
"config": {
"url": "{YOUR_WEBHOOK_URL}"
}
}
}'
You will see a response similar to the following:
{
"id": "web_oPymMJ0isyuS",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-20T12:42:56.433Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:44.096Z",
"paused_at": null,
"name": "account-123-endpoint-123",
"rules": [],
"description": null,
"destination": {
"id": "des_wNYxQXpkYHcM",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"type": "HTTP",
"config": {
"url": "{YOUR_WEBHOOK_URL}",
"rate_limit": null,
"rate_limit_period": "second",
"path_forwarding_disabled": false,
"http_method": null,
"auth_type": "HOOKDECK_SIGNATURE",
"auth": {}
},
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-20T12:42:56.250Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.903Z",
"name": "endpoint-123",
"description": null
},
"source": {
"id": "src_KUdNgMByl0uP",
"team_id": "tm_SAN9hnAiGLbI",
"disabled_at": null,
"updated_at": "2023-11-20T12:42:56.252Z",
"created_at": "2023-11-18T16:52:43.905Z",
"name": "account-123",
"type": "HTTP",
"config": {
"allowed_http_methods": ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"],
"custom_response": null,
"auth_type": null,
"auth": null
},
"description": null,
"url": "https://hkdk.events/v1/publish"
},
"full_name": "account-123 -> account-123-endpoint-123"
}
Publish another webhook event via Hookdeck to the developer's webhook URL.
curl --location 'https://hkdk.events/v1/publish' \
--header 'X-Hookdeck-Source-Name: account-123' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PROJECT_API_KEY" \
--data-raw '{
"type": "order.updated",
"timestamp": "2023-11-18 17:25:15",
"email": "customer@example.com",
"description": "Hookdeck Growth plan",
"plan_id": "growth",
"payment_status": "paid"
}'
As before, you can check this in both the Hookdeck dashboard Requests and Events sections.
What you have learned
By following this quickstart, you set up a Connection with Hookdeck and tested sending webhooks to Hookdeck's Mock API endpoint. You then ran a local development server and used the Hookdeck CLI to send and receive webhooks to your local environment. Finally, you updated the Connection to deliver webhooks to a live deployed application.
Where next?
You've just scratched the surface of Hookdeck. So, try out the following features:
- Authenticate the sending of webhooks by adding source authentication.
- Set up a rate limit on your Destination to manage the number of requests your customer's server has to manage per second.
- Define your retry logic for those occasions when your customer's deployed application isn't available or can't accept a webhook request.
- Create a second connection that uses the same source to deliver a webhook to two customer endpoints from a single event.