How to Test and Replay GitHub Webhook Events on localhost with Hookdeck
GitHub is a popular version control platform for developers that allows them to collaborate on code and monitor changes to their projects. GitHub provides webhooks, which allow developers to set up events that trigger a POST request to a given URL. This allows external apps to be alerted of repository changes and take appropriate action.
Hookdeck is a webhook management platform that helps developers reliably receive webhooks, manage events, and troubleshoot any issues quickly. It also provides the ability to expose a localhost server to the internet. This is useful for testing webhooks, as it allows developers to receive webhook requests from a service like GitHub on their local development environment.
In this article, I discuss how to test GitHub webhooks with a localhost Node.js Express application using Hookdeck.
Relaying your GitHub webhooks through Hookdeck provides an overall view and keeps track of every event that occurs.
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure a localhost Node.js Express server and use Hookdeck to expose it to the internet. Then, we'll set up a GitHub webhook to send requests to the localhost server. We will cover how to:
- Set up a localhost webhook endpoint
- Create a Hookdeck connection
- Create a GitHub webhook
- Test GitHub webhook event to localhost app
Set up a localhost webhook endpoint
For this example, we are going to use the sample Node.js code from Hookdeck's repository. Feel free to follow up with any application or code you might have.
- Open up your terminal and clone the repository by running:
git clone https://github.com/hookdeck/nodejs-webhook-server-example.git
- Change into the cloned directory and install the dependencies.
cd nodejs-webhook-server-example
npm install
- Start the server by executing:
npm start
The Node.js server starts up on
http://localhost:1337. See the list of endpoints in thesrc/routes.tsfile. We will make use of the/github-webhooks-endpoint.
Create a Hookdeck connection
There are several ways of creating a Hookdeck connection (see the guide here).
Create a Hookdeck connection with Hookdeck CLI
- Install the Hookdeck CLI.
- Open up your terminal and expose the localhost port with:
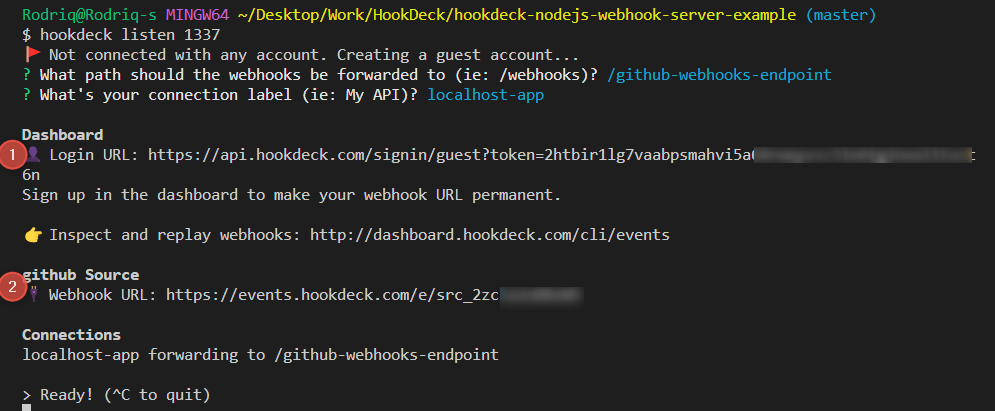
hookdeck listen 1337
- The Hookdeck CLI initiates the creation of a guest account that will be used.
- You get prompted to do some basic setup:
- Create a new source (ex. GitHub)
- Set the path to be forwarded to as
/github-webhooks-endpoint - Name the connection label (ex. localhost-app)
- The connection is created and you are given:
- A login URL to use for your Hookdeck dashboard
- The webhook URL needed
- The same connection can be seen on your Hookdeck online dashboard after following the link.
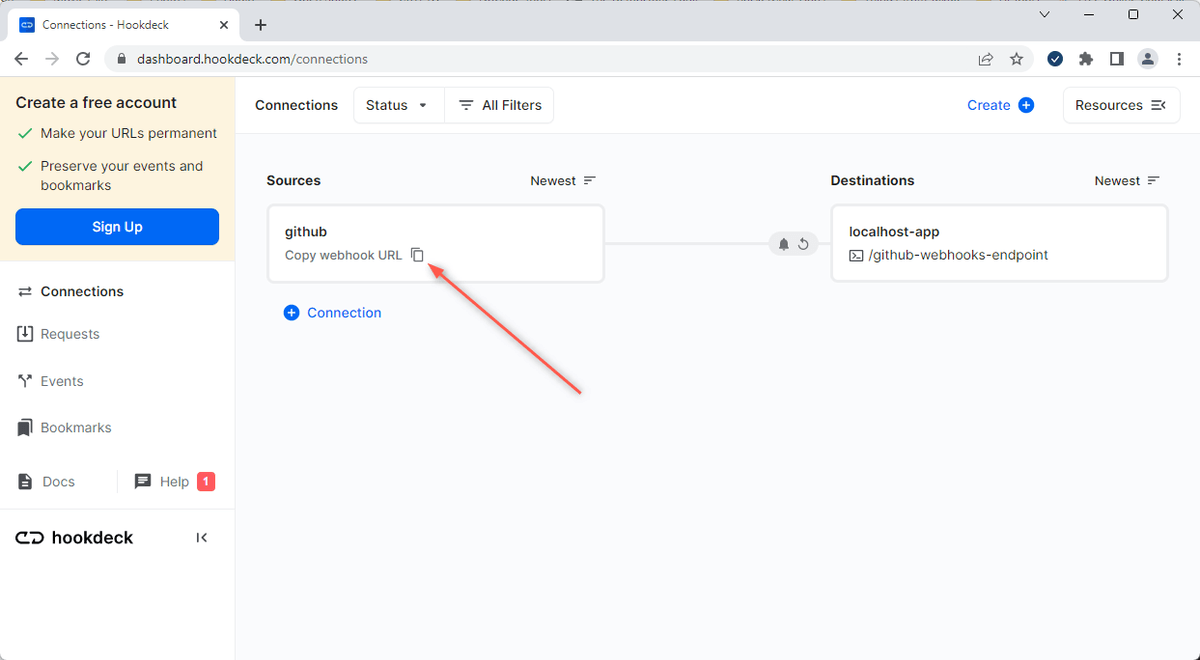
- Copy the GitHub source webhook URL. It will be used later in setting up the GitHub webhook listener
Create a GitHub webhook
To create a GitHub webhook:
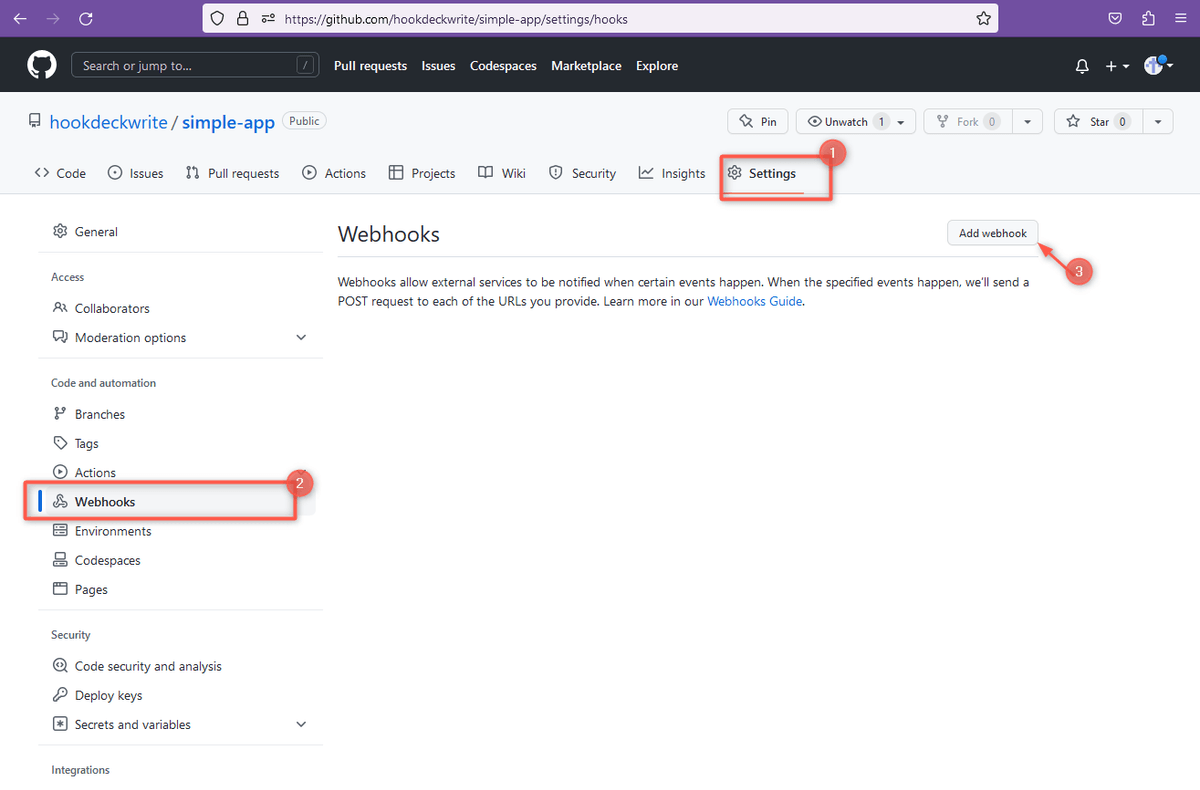
- Create or open an existing GitHub repository.
- Navigate to Settings > Webhooks.
- Click on Add webhook to add a new webhook.
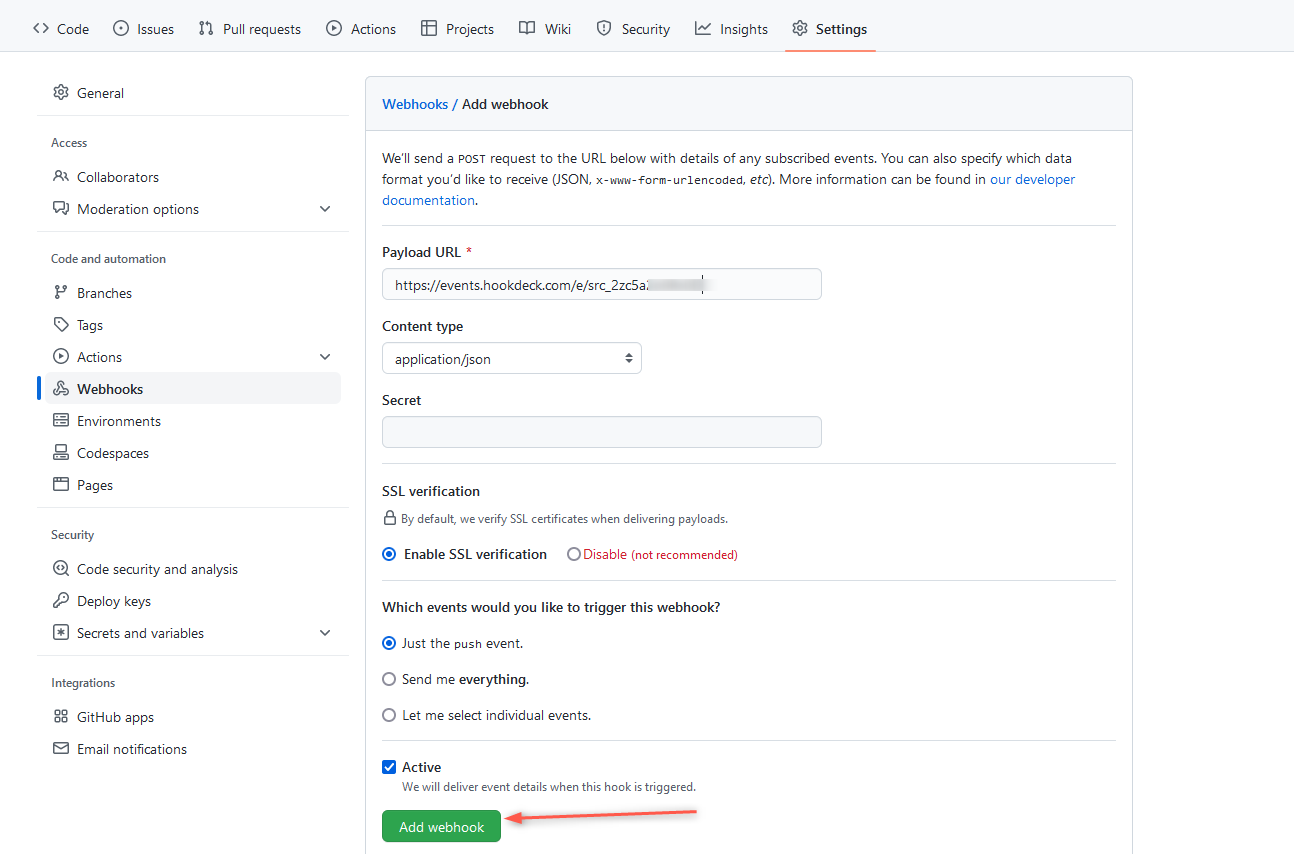
- In the Payload URL field, enter the Hookdeck endpoint URL and set the content type to
application/json. - Select the events you want to trigger the webhook, such as Push or Pull request and then Add webhook.
Now, when the specified events occur (push) in the repository, GitHub will send a POST request to the Hookdeck endpoint URL, which will forward the request to your localhost Node.js Express server.
Test GitHub webhook event to localhost app
We have successfully set up our localhost server, created a Hookdeck connection, and configured a GitHub webhook. Let us test and trigger the event specified to make sure it is being received in our localhost application.
By default, GitHub sends a ping payload to test out the webhook created.
The webhook event can be triggered through any of the following events supported by GitHub.
- Upon a successful GitHub webhook event trigger, the payload gets relayed by Hookdeck directly to your localhost application.
- On your Hookdeck Request dashboard, filter the request sources to GitHub. You should see the requests received with a
200status code.
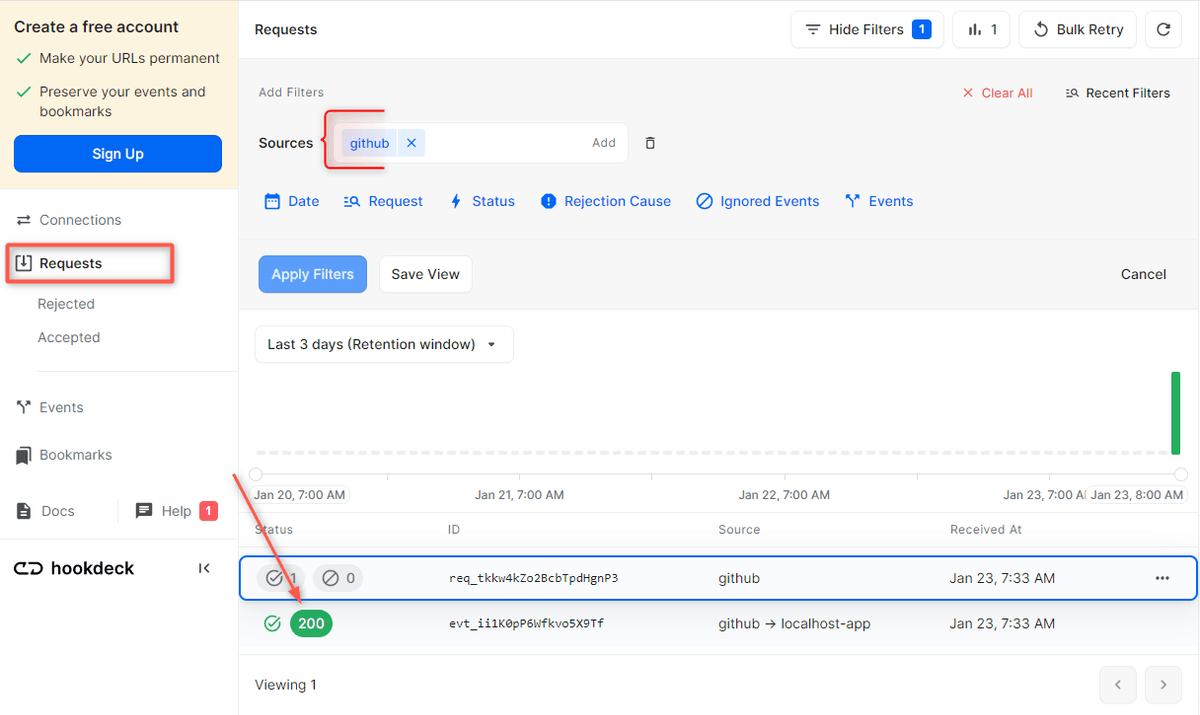
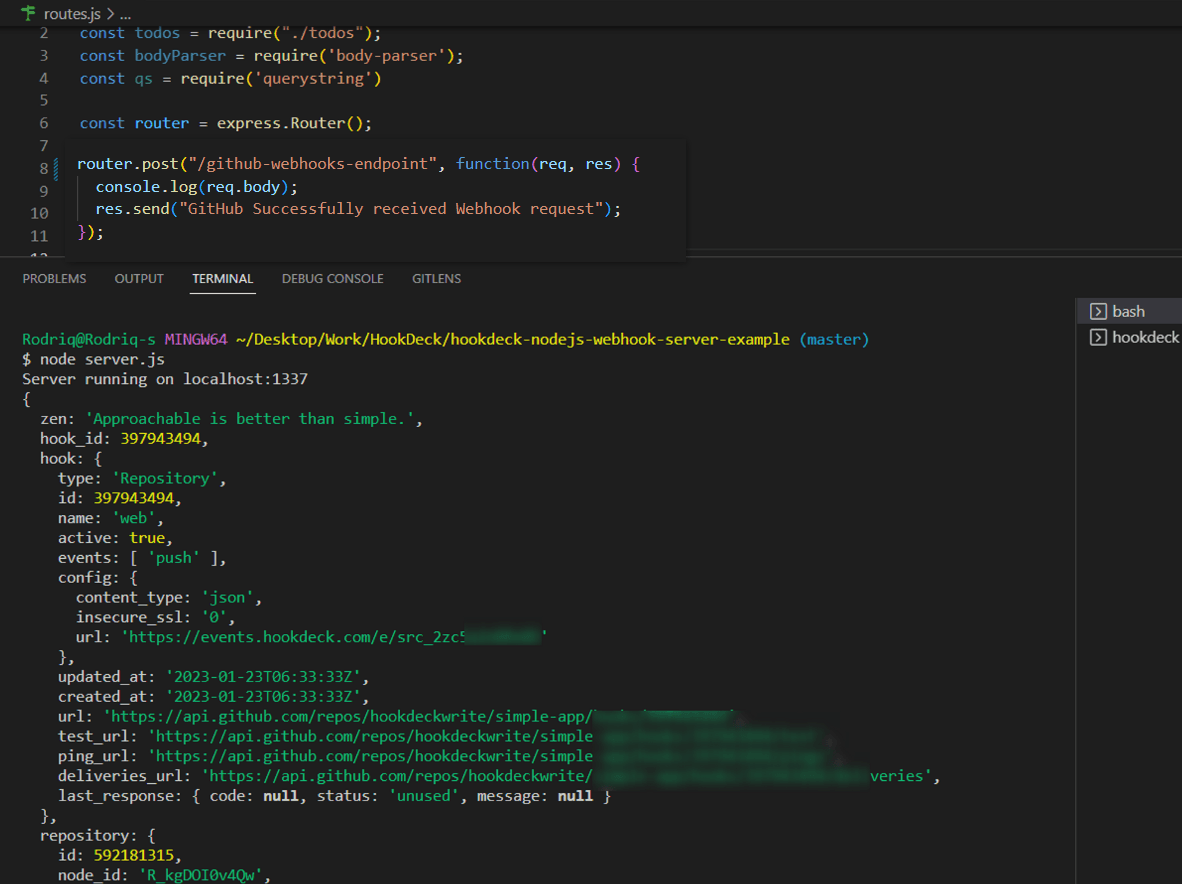
- Back in the terminal of the localhost application, the successful payload from the webhook is received and logged.
Retrying error or failed events
In case any failed events don’t make it to your destination for some reason, Hookdeck provides you with the ability to retry any attempts to deliver any failed or error event.
To retry a failed event:
- Navigate to the Events tab on the sidebar of your Hookdeck dashboard and filter as per your Destination then hit the Retry across the failed event.
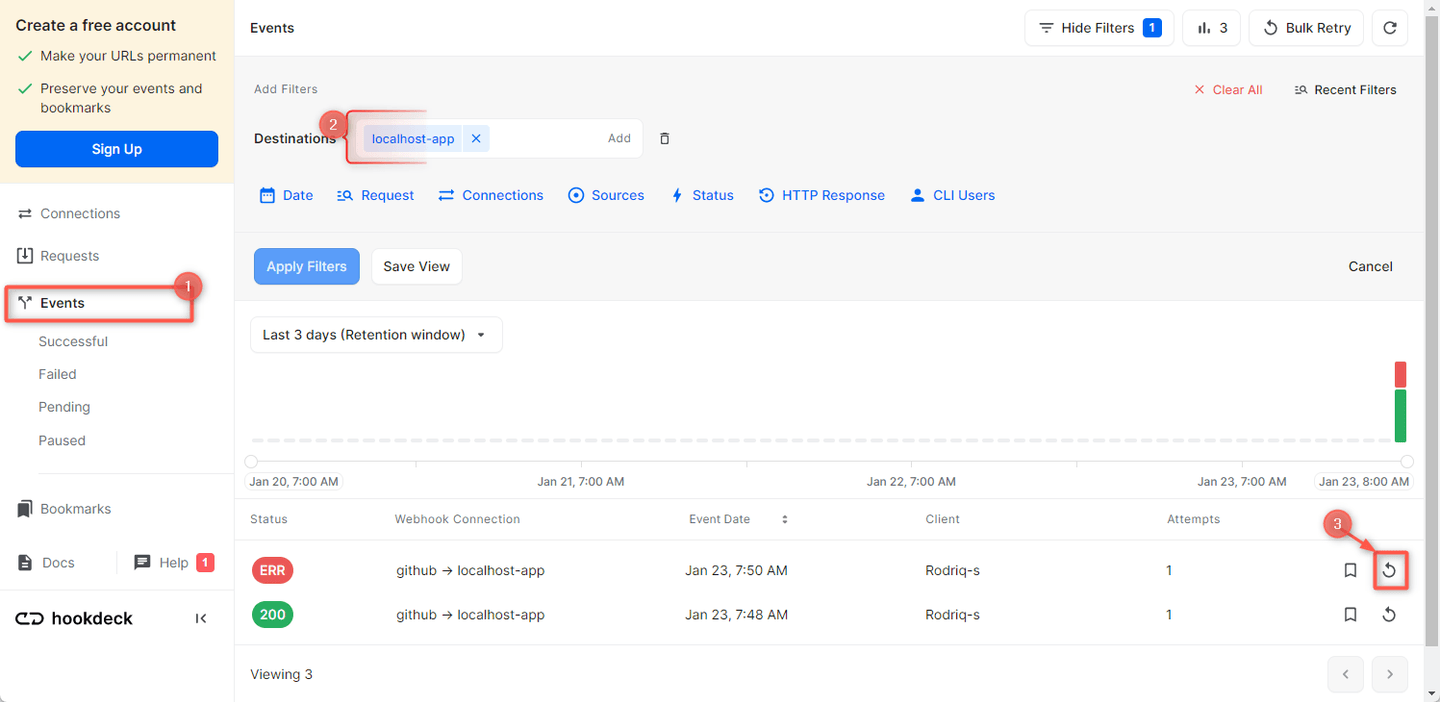
- This replays the event again from Hookdeck to the local application.
A Hookdeck Request is an incoming webhook that Hookdeck receives from an external source. It contains the data that was sent by the external source as is (ex. from GitHub).
A Hookdeck Event is the webhook delivered by Hookdeck including configurations or filters applied to a destination (ex. to Localhost app).
See more details on managing Hookdeck requests and events on the Hookdeck documentation.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned how to receive GitHub webhook events through Hookdeck, a webhook infrastructure for reliable ingestion, to an application running on localhost.
Hookdeck can be used safely to consume, monitor, and troubleshoot your GitHub webhooks. For more details, see our guide to GitHub webhooks features and best practices.
